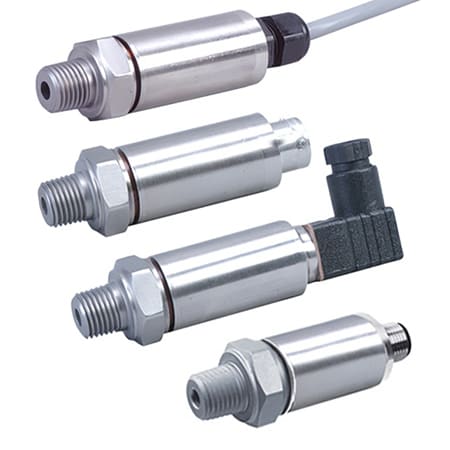
A pressure transducer is a device that measures the pressure of a fluid, indicating the force the fluid is exerting on surfaces in contact with it. Pressure transducers are used in many control and monitoring applications such as flow, air speed, level, pump systems or altitude.
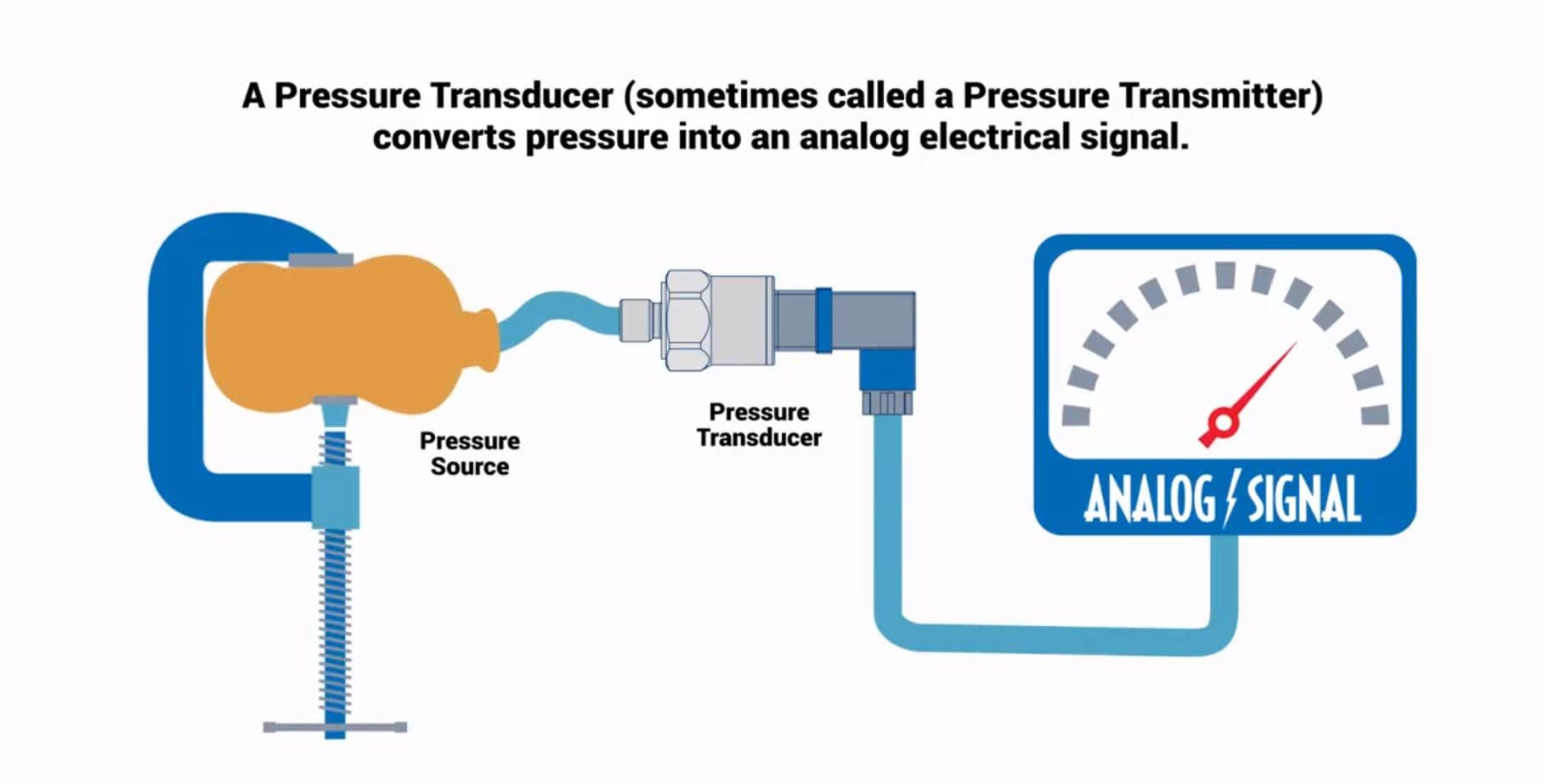
To calculate pressure, the pressure transducer contains a force collector such as a flexible diaphragm which deforms when pressurized and a transduction element that transforms this deformation into an electrical signal. The shape and methods of transductions are optimized to the requirements of the process that is being measured.
How Does a Pressure sensor Work?: Componentry
The most common pressure transducer constructions include a force collector such as a flexible diaphragm and a transduction element that uses a dependent resistive, capacitive, or inductive method to generate an electrical signal. The type of electrical device used will determine the components used to build the pressure sensor.
What does a pressure transducer measure?
A pressure transducer measures pressure. It uses a sensor capable of converting the pressure acting on it into electrical signals. These electrical signals are then relayed to controllers or PLCs where they are then processed and recorded.Pressure transducers use strain gauges to measure the force acting on them. The strain gauges undergo deformation and this creates a change in voltage produced by it. The pressure measurement is based on the degree of change seen in the voltage.
There are also advanced versions of pressure transducers that use capacitance or piezoelectric sensors instead of the strain gauges. They are chosen based on the range, work environment and precision required from the pressure sensor.
How static pressure transmitter works?
Static pressure transducers measure the pressure of a fluid when it is at rest. Static pressure transducers are the most commonly used pressure monitoring devices.When a fluid exerts pressure on the pressure transducers, the strain gage (or the sensor) within it gets deformed. This deformation results in voltage variations. The magnitude of variation corresponds to the intensity of the pressure. Once the pressure releases, the strain gauge gets back to its original form.
Piezoelectric pressure transducers are an example of non-static or dynamic pressure transducers. They cannot measure static pressure, instead, they measure pressure variances in real-time.
Piezoresistive strain gauge Pressure Transducer
A typical piezoresistive strain gauge pressure transducer utilizes strain gauges bonded to a flexible diaphragm so that any change in pressure causes a small deformation, or strain, in the diaphragm material. The deformation changes the resistance of the strain gauges, typically arranged as a Wheatstone bridge, providing a convenient conversion of the pressure measurement into useable electrical signal.
Capacitance Pressure Transducer
A variable capacitance pressure transducer has a capacitive plate (diaphragm) and another capacitive plate (electrode) fixed to an unpressurized surface with a gap of a certain distance between the diaphragm and the electrode. A change in pressure will widen or narrow the gap between the two plates which varies the capacitance. This change in capacitance is then converted into a usable signal.
Pressure Measurement: Types of Pressure
There are three defined pressure references for measuring pressure. While there are other types, like vacuum or sealed gage, all can be classified into these three categories. With diaphragm type pressure sensors, it is easiest to understand the reference pressure as the pressure that is exerted on the other side of the diaphragm from the process being measured.
Absolute pressure
Measures the pressure relative to a perfect vacuum, using absolute zero as a reference point. An example is a barometric pressure transducer. These also include sealed gauge, where the signal has been offset to match the gauge pressure at the time of construction.
Gauge pressure
Measures the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. An example of this is a tire pressure sensor. Also includes vacuum sensors, whose signals are reversed so that they signal positive when the measured pressure is below atmospheric pressure.
Differential pressure
Measures the difference between two pressures on each side of the sensor. An example is a liquid pressure transducer where the fluid levels above and below the liquid are measured.
Types of Pressure Signal Outputs
When connected to an electrical source and a pressure source, a pressure transducer will produce an electrical output signal proportional to the pressure. This may be voltage, current, or frequency. There are four different output parameters available. Below is a summary of the outputs and when they are best used.
Digital Pressure Transducer:
A digital signal provides more versatility than analog signals, often they are called smart devices, because they provide greater functionality then other sensor types.Smart sensors can often describe their location, calibration information, log data, detect unusual events, or activate alarms. When choosing a digital output, because there are many communication protocols available, it’s important to select a protocol that is compatible with the system you are using. Depending on the protocol the transmission distances can be more than a mile.
Best use: Long transmission distances, smart sensing.
Millivolt Output Pressure sensor (ratiometric):
The actual output is directly proportional to the pressure transducer input power or excitation. If the excitation fluctuates, the output will also change. Because of its dependence on the excitation level, regulated power supplies are suggested for use with millivolt transducers.The sensor should not be in an electrically noisy environment because the output signal is so low. However, these devices can easily handle harsher environments than other output types due to the output’s lack of signal conditioning stage and its compact design.
Best use: When it’s a short distance between the transducer and the readout instrument, there is minimal electrical noise, or a more durable pressure sensor is required to withstand a harsh environment.
Voltage Pressure tramsitter:
In this type of pressure sensor, the output is normally 0-5dc or 0-10Vdc and provides a higher output than a millivolt transducer due to its integral signal condition.Although model specific, the output of the transducer is not normally a direct function of excitation. This means unregulated power supplies are often enough as long as they fall within a specified power range. They have a higher-level output and are therefore not as susceptible to electrical noise as millivolt transducers.
Best use: Industrial environments where electrical noise may be present.
mA Output Pressure transmitter:
The mA is the most common output in use. The signal can vary from 0 to 4 mA to 20 mA and is designed as a two-wire installation where the power supply lines provide voltage to the transducer and the transducer controls the current in the circuit to generate the signal.This configuration makes the signal more immune to electrical interference and allows long cable runs exceeding 1000 feet.
Best use: Environments with high electrical interference or where long transmission distances are needed.


